

After swallowing her food, it seems stuck in her throat and chest. She feels her heart race and pounding in her chest. She immediately freezes, the food in her mouth begins to feel like a wad of dry hay, and she nearly gags as she tries to swallow it. Jayla is sitting, having an outdoor lunch with friends when a large spider lands on her plate. Much of the function of the autonomic system is based on the connections within an autonomic, or visceral, reflex.” The Autonomic Nervous System at Work The digestive system has a big job to do. Besides the fight-or-flight response, there are the responses referred to as “rest and digest”. However, the autonomic nervous system is not just about responding to threats. In fact, the adaptations of the autonomic nervous system probably predate the human species and are likely to be common to all mammals, and perhaps shared by many animals. It is engrained in the nervous system to respond like this. In the modern world, these sorts of reactions are associated with anxiety as much as with response to a threat. The autonomic nervous system is tied into emotional responses and the fight-or-flight response sounds like a panic attack. Differentiate between the functions, target organs and neurotransmitters used by the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system.Compare and contrast the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the nervous system.Upon completion of the work in this chapter students should be able to:
#Effectors of the somatic nervous system license
Photo by Yitzilitt on Wikimedia Commons, license CC-BY-SA. Figure 15.1 Hand of a person with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) and dysautonomia exhibiting blood pooling after standing for too long in cold weather. The more common forms of these conditions include Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome POTS / Orthostatic Intolerance OI (Figure 15.1), Neurocardiogenic Syncope NCS, Pure Autonomic Failure PAF and Multiple Systems Atrophy MSA.
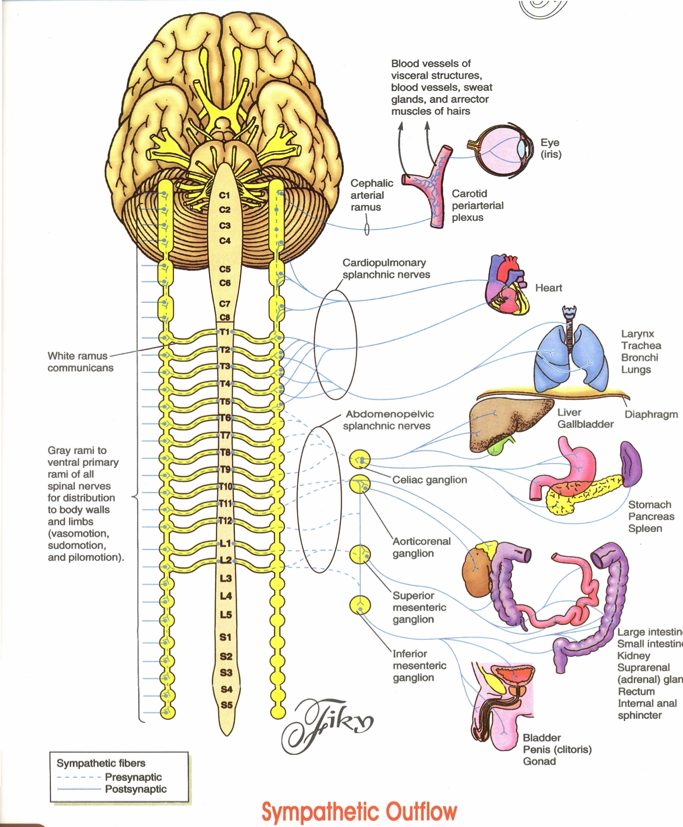
Over one million Americans are impacted with a primary autonomic system disorder. Other symptoms include fatigue, lightheadedness, feeling faint or passing out (syncope), weakness and cognitive impairment.Īutonomic dysfunction can occur as a secondary condition of another disease process, like diabetes, or as a primary disorder where the autonomic nervous system is the only system impacted. Symptoms are wide ranging and can include problems with the regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature and perspiration.
For this reason, dysautonomia patients often present with numerous, seemingly unrelated maladies. Abnormal functioning of the autonomic nervous system can be life threatening and there is a specific term for it: dysautonomia. Dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system can produce the apparent malfunction of the organs it regulates.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
